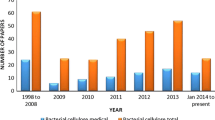
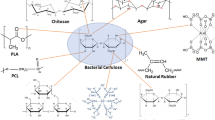
Abstract
Cellulose, the most abundant polysaccharide on earth, can be obtained from various sources including the cell wall of plants and woods, bacteria, algae, and tunicates. However, the cellulose obtained from bacteria known as bacterial cellulose or bacterial nanocellulose (BC) has gained major popularity due to its simple production process, non–toxicity, high purity, and biocompatibility. Furthermore, the BC holds distinct properties like higher crystallinity, larger surface area, high porosity, great water holding capacity, and enhanced tensile strength. These unique features of BC further widen its application in several areas including drug delivery, tissue engineering, wound dressing, etc. The present review summarizes the recent developments in BC production and its biomedical applications. Firstly, the microorganisms involved, various medium compositions used and the methods adopted for BC production are discussed, and then reactors used for industrial production of BC are introduced. Subsequently, the applications of BC in tissue engineering, drug delivery system, and pharmaceutical & medical sectors are discussed in detail. Finally, the future perspective of BC in biomedical applications is discussed in brief.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arena M, Abbate C, Fukushima K, Gennari M (2011) Degradation of poly (lactic acid) and nanocomposites by Bacillus licheniformis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18(6):865–870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0443-2
de Paula FC, de Paula CB, Contiero J (2018) Prospective biodegradable plastics from biomass conversion processes. In: Biernat K (ed) Biofuels—state of development. IntechOpen, London, pp 245–271. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.75111
Pradhan S, Dikshi PK, Moholkar VS (2020) Production, characterization, and applications of biodegradable polymer: Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Advances in Sustainable Polymers. Springer, Singapore, pp 51–94
Swingler S, Gupta A, Gibson H, Kowalczuk M, Heaselgrave W, Radecka I (2021) Recent advances and applications of bacterial cellulose in biomedicine. Polymers 13(3):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13030412
Poddar MK, Dikshit PK (2021) Recent development in bacterial cellulose production and synthesis of cellulose based conductive polymer nanocomposites. Nano Select 2(9):1605–1628. https://doi.org/10.1002/nano.202100044
Dikshit PK, Kim BS (2020) Bacterial cellulose production from biodiesel–derived crude glycerol, magnetic functionalization, and its application as carrier for lipase immobilization. Int J Biol Macromol 153:902–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.047
Campano C, Balea A, Blanco A, Negro C (2016) Enhancement of the fermentation process and properties of bacterial cellulose: a review. Cellulose 23(1):57–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0802-0
Brown AJ (1886) XLIII.—On an acetic ferment which forms cellulose. J Chem Soc Trans 49:432–439
Liu W, Du H, Zhang M, Liu K, Liu H, Xie H, Zhang X, Si C (2020) Bacterial cellulose–based composite scaffolds for biomedical applications: a review. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(20):536–7562. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00125
Gatenholm P, Klemm D (2010) Bacterial nanocellulose as a renewable material for biomedical applications. MRS bull 35(3):208–213. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs2010.653
Lay M, González I, Tarrés JA, Pellicer N, Bun KN, Vilaseca F (2017) High electrical and electrochemical properties in bacterial cellulose/polypyrrole membranes. Eur Polym J 91:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2017.03.021
Islam SU, Ul–Islam M, Ahsan H, Ahmed MB, Shehzad A, Fatima A, Sonn JK, Lee YS, (2021) Potential applications of bacterial cellulose and its composites for cancer treatment. Int J Biol Macromol 168:301–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.042
Purwidyantri A, Karina HCH, Srikandace Y, Prabowo BA, Lai CS (2020) Facile bacterial cellulose nanofibrillation for the development of a plasmonic paper sensor. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 6(5):3122–3131. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01890
Seddiqi H, Oliaei E, Honarkar H, Jin J, Geonzon LC, Bacabac RG, Klein-Nulend J (2021) Cellulose and its derivatives: towards biomedical applications. Cellulose 28(4):1893–1931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03674-w
Lin SP, Loira Calvar I, Catchmark JM, Liu JR, Demirci A, Cheng KC (2013) Biosynthesis, production and applications of bacterial cellulose. Cellulose 20(5):2191–2219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9994-3
Castro C, Zuluaga R, Álvarez C, Putaux JL, Caro G, Rojas OJ, Mondragon I, Gañán P (2012) Bacterial cellulose produced by a new acid–resistant strain of Gluconacetobacter genus. Carbohydr Polym 89(4):1033–1037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.03.045
Yamada Y, Yukphan P, Vu HTL, Muramatsu Y, Ochaikul D, Tanasupawat S, Nakagawa Y (2012) Description of Komagataeibacter gen. nov., with proposals of new combinations (Acetobacteraceae). J Gen Appl Microbiol 58(5):397–404. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.58.397
Pfeffer S, Mehta K, Brown RM Jr (2016) Complete genome sequence of a Gluconacetobacter hansenii ATCC 23769 isolate, AY201, producer of bacterial cellulose and important model organism for the study of cellulose biosynthesis. Genome Announc 4(4):e00808-e816. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00808-16
Sperotto G, Stasiak LG, Godoi JPMG, Gabiatti NC, De Souza SS (2021) A review of culture media for bacterial cellulose production: complex, chemically defined and minimal media modulations. Cellulose 28(5):2649–2673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03754-5
Lee KY, Buldum G, Mantalaris A, Bismarck A (2014) More than meets the eye in bacterial cellulose: biosynthesis, bioprocessing, and applications in advanced fiber composites. Macromol Biosci 14(1):10–32. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.201300298
Singhania RR, Patel AK, Tsai ML, Chen CW, Di Dong C (2021) Genetic modification for enhancing bacterial cellulose production and its applications. Bioengineered 12(1):6793–6807. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1968989
Urbina L, Hernández-Arriaga AM, Eceiza A, Gabilondo N, Corcuera MA, Prieto MA, Retegi A (2017) By–products of the cider production: an alternative source of nutrients to produce bacterial cellulose. Cellulose 24(5):2071–2082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1263-4
Halib N, Ahmad I, Grassi M, Grassi G (2019) The remarkable three–dimensional network structure of bacterial cellulose for tissue engineering applications. Int J Pharm 566:631–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.06.017
Hur DH, Rhee HS, Lee JH, Shim WY, Kim TY, Lee SY, Park JH, Jeong KJ (2020) Enhanced production of cellulose in Komagataeibacter xylinus by preventing insertion of IS element into cellulose synthesis gene. Biochem Eng J 156:107527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2020.107527
Liu M, Li S, Xie Y, Jia S, Hou Y, Zou Y, Zhong C (2018) Enhanced bacterial cellulose production by Gluconacetobacter xylinus via expression of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin and oxygen tension regulation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(3):1155–1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8680-z
Jacek P, Ryngajłło M, Bielecki S (2019) Structural changes of bacterial nanocellulose pellicles induced by genetic modification of Komagataeibacter hansenii ATCC 23769. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(13):5339–5353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09846-4
Kuo CH, Teng HY, Lee CK (2015) Knock–out of glucose dehydrogenase gene in Gluconacetobacter xylinus for bacterial cellulose production enhancement. Biotechnol Bioproc E 20(1):18–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-014-0316-x
Shigematsu T, Takamine K, Kitazato M, Morita T, Naritomi T, Morimura S, Kida K (2005) Cellulose production from glucose using a glucose dehydrogenase gene (gdh)–deficient mutant of Gluconacetobacter xylinus and its use for bioconversion of sweet potato pulp. J Biosci Bioeng 99(4):415–422. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.99.415
Jacek P, Dourado F, Gama M, Bielecki S (2019) Molecular aspects of bacterial nanocellulose biosynthesis. Microb Biotechnol 12(4):633–649. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13386
Fang J, Kawano S, Tajima K, Kondo T (2015) In vivo curdlan/cellulose bionanocomposite synthesis by genetically modified Gluconacetobacter xylinus. Biomacromol 16(10):3154–3160. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.5b01075
Yadav V, Paniliatis BJ, Shi H, Lee K, Cebe P, Kaplan DL (2010) Novel in vivo–degradable cellulose–chitin copolymer from metabolically engineered Gluconacetobacter xylinus. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(18):6257–6265. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00698-10
Jozala AF, de Lencastre-Novaes LC, Lopes AM, de Carvalho Santos-Ebinuma V, Mazzola PG, Pessoa A Jr, Grotto D, Gerenutti M, Chaud MV (2016) Bacterial nanocellulose production and application: a 10-year overview. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(5):2063–2072. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7243-4
Hestrin S, Schramm MJBJ (1954) Synthesis of cellulose by Acetobacter xylinum. 2. Preparation of freeze–dried cells capable of polymerizing glucose to cellulose. Biochem J 58(2):345. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj0580345
Heo MS, Son HJ (2002) Development of an optimized, simple chemically defined medium for bacterial cellulose production by Acetobacter sp. A9 in shaking cultures. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 36(1):41–45. https://doi.org/10.1042/ba20020018
de Souza SS, Berti FV, de Oliveira KP, Pittella CQ, de Castro JV, Pelissari C, Rambo CR, Porto LM (2019) Nanocellulose biosynthesis by Komagataeibacter hansenii in a defined minimal culture medium. Cellulose 26(3):1641–1655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2178-4
Deshmukh AR, Dikshit PK, Kim BS (2022) Green in situ immobilization of gold and silver nanoparticles on bacterial nanocellulose film using Punica granatum peels extract and their application as reusable catalysts. Int J Biol Macromol 205:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.02.064
Cao Y, Lu S, Yang Y (2018) Production of bacterial cellulose from byproduct of citrus juice processing (citrus pulp) by Gluconacetobacter hansenii. Cellulose 25(12):6977–6988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2056-0
Zhao H, Xia J, Wang J, Yan X, Wang C, Lei T, Xian M, Zhang H (2018) Production of bacterial cellulose using polysaccharide fermentation wastewater as inexpensive nutrient sources. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 32(2):350–356. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2017.1418673
Machado RT, Meneguin AB, Sabio RM, Franco DF, Antonio SG, Gutierrez J, Tercjak A, Berretta AA, Ribeiro SJ, Lazarini SC, Barud HS (2018) Komagataeibacter rhaeticus grown in sugarcane molasses–supplemented culture medium as a strategy for enhancing bacterial cellulose production. Ind Crop Prod 122:637–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.06.048
Fan X, Gao Y, He W, Hu H, Tian M, Wang K, Pan S (2016) Production of nano bacterial cellulose from beverage industrial waste of citrus peel and pomace using Komagataeibacter xylinus. Carbohydr Polym 151:1068–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.06.062
Revin V, Liyaskina E, Nazarkina M, Bogatyreva A, Shchankin M (2018) Cost–effective production of bacterial cellulose using acidic food industry by–products. Braz J Microbiol 49:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2017.12.012
Jahan F, Kumar V, Saxena RK (2018) Distillery effluent as a potential medium for bacterial cellulose production: a biopolymer of great commercial importance. Bioresour Technol 250:922–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.094
Dubey S, Singh J, Singh RP (2018) Biotransformation of sweet lime pulp waste into high–quality nanocellulose with an excellent productivity using Komagataeibacter europaeus SGP37 under static intermittent fed–batch cultivation. Bioresour Technol 247:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.089
Kiziltas EE, Kiziltas A, Gardner DJ (2015) Synthesis of bacterial cellulose using hot water extracted wood sugars. Carbohydr Polym 124:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.01.036
Bilgi E, Bayir E, Sendemir-Urkmez A, Hames EE (2016) Optimization of bacterial cellulose production by Gluconacetobacter xylinus using carob and haricot bean. Int J Biol Macromol 90:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.02.052
Huang C, Guo HJ, Xiong L, Wang B, Shi SL, Chen XF, Lin XQ, Wang C, Luo J, Chen XD (2016) Using wastewater after lipid fermentation as substrate for bacterial cellulose production by Gluconacetobacter xylinus. Carbohydr Polym 136:198–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.043
Güzel M, Akpınar Ö (2019) Production and characterization of bacterial cellulose from citrus peels. Waste Biomass Valori 10(8):2165–2175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0241-x
Algar I, Fernandes SC, Mondragon G, Castro C, Garcia-Astrain C, Gabilondo N, Retegi A, Eceiza A (2015) Pineapple agroindustrial residues for the production of high value bacterial cellulose with different morphologies. J Appl Polym Sci 132(1):41237. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41237
Pacheco G, Nogueira CR, Meneguin AB, Trovatti E, Silva MC, Machado RT, Ribeiro SJ, Da Silva Filho EC, Barud HDS (2017) Development and characterization of bacterial cellulose produced by cashew tree residues as alternative carbon source. Ind Crop Prod 107:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.05.026
Lotfiman S, Awang Biak DR, Ti TB, Kamarudin S, Nikbin S (2018) Influence of date syrup as a carbon source on bacterial cellulose production by Acetobacter xylinum 0416. Adv Polym Tech 37(4):1085–1091. https://doi.org/10.1002/adv.21759
Kuo CH, Huang CY, Shieh CJ, Wang HMD, Tseng CY (2019) Hydrolysis of orange peel with cellulase and pectinase to produce bacterial cellulose using Gluconacetobacter xylinus. Waste Biomass Valori 10(1):85–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0034-7
Kumbhar JV, Rajwade JM, Paknikar KM (2015) Fruit peels support higher yield and superior quality bacterial cellulose production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(16):6677–6691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6644-8
Cerrutti P, Roldán P, García RM, Galvagno MA, Vázquez A, Foresti ML (2016) Production of bacterial nanocellulose from wine industry residues: Importance of fermentation time on pellicle characteristics. J Appl Polym Sci 133(14):43109. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43109
Guo X, Chen L, Tang J, Jönsson LJ, Hong FF (2016) Production of bacterial nanocellulose and enzyme from [AMIM] Cl-pretreated waste cotton fabrics: effects of dyes on enzymatic saccharification and nanocellulose production. J Chem Technol Biot 91(5):1413–1421. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4738
Soemphol W, Hongsachart P, Tanamool V (2018) Production and characterization of bacterial cellulose produced from agricultural by–product by Gluconacetobacter strains. Mater Today: Proc 5(5):11159–11168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.01.036
Pang M, Huang Y, Meng F, Zhuang Y, Liu H, Du M, Ma Q, Wang Q, Chen Z, Chen L, Cai Y (2020) Application of bacterial cellulose in skin and bone tissue engineering. Eur Polym J 122:109365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.109365
Krystynowicz A, Czaja W, Wiktorowska-Jezierska A, Gonçalves-Miśkiewicz M, Turkiewicz M, Bielecki S (2002) Factors affecting the yield and properties of bacterial cellulose. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 29(4):189–195. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.7000303
Huang Y, Zhu C, Yang J, Nie Y, Chen C, Sun D (2014) Recent advances in bacterial cellulose. Cellulose 21(1):1–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0088-z
Wu SC, Li MH (2015) Production of bacterial cellulose membranes in a modified airlift bioreactor by Gluconacetobacter xylinus. J Biosci Bioeng 120(4):444–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2015.02.018
Chao Y, Ishida T, Sugano Y, Shoda M (2000) Bacterial cellulose production by Acetobacter xylinum in a 50-L internal-loop airlift reactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 68(3):345–352. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(20000505)68:3%3c345::AID-BIT13%3e3.0.CO;2-M
Song HJ, Li H, Seo JH, Kim MJ, Kim SJ (2009) Pilot–scale production of bacterial cellulose by a spherical type bubble column bioreactor using saccharified food wastes. Korean J Chem Eng 26(1):141–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0022-0
Serafica G, Mormino R, Bungay H (2002) Inclusion of solid particles in bacterial cellulose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58(6):756–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-0978-8
Lin SP, Hsieh SC, Chen KI, Demirci A, Cheng KC (2014) Semi–continuous bacterial cellulose production in a rotating disk bioreactor and its materials properties analysis. Cellulose 21(1):835–844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0136-8
Lin SP, Liu CT, Hsu KD, Hung YT, Shih TY, Cheng KC (2016) Production of bacterial cellulose with various additives in a PCS rotating disk bioreactor and its material property analysis. Cellulose 23(1):367–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0855-0
Lu H, Jiang X (2014) Structure and properties of bacterial cellulose produced using a trickling bed reactor. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172(8):3844–3861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0795-4
Cheng KC, Catchmark JM, Demirci A (2011) Effects of CMC addition on bacterial cellulose production in a biofilm reactor and its paper sheets analysis. Biomacromol 12(3):730–736. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm101363t
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink HP, Bohn A (2005) Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew Chem Int Edit 44(22):3358–3393. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200460587
Updegraff DM (1969) Semimicro determination of cellulose inbiological materials. Anal Biochem 32(3):420–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2697(69)80009-6
Deguchi S, Tsujii K, Horikoshi K (2006) Cooking cellulose in hot and compressed water. Chem Commun 31:3293–3295. https://doi.org/10.1039/b605812d
Peng BL, Dhar N, Liu HL, Tam KC (2011) Chemistry and applications of nanocrystalline cellulose and its derivatives: a nanotechnology perspective. Can J Chem Eng 89(5):1191–1206. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.20554
Einchhorn SJ, Dufresne A, Aranguren MM, Capadona JR, Rowan SJ, Weder C, Veigel S (2010) Review: current international research into cellulose nanofibres and composites. J Mater Sci 45:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3874-0
Michelin M, Gomes DG, Romaní A, Polizeli MDL, Teixeira JA (2020) Nanocellulose production: exploring the enzymatic route and residues of pulp and paper industry. Molecules 25(15):3411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25153411
Aulin C, Gällstedt M, Lindström T (2010) Oxygen and oil barrier properties of microfibrillated cellulose films and coatings. Cellulose 17(3):559–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-009-9393-y
Brown EE, Hu D, Abu Lail N, Zhang X (2013) Potential of nanocrystalline cellulose–fibrin nanocomposites for artificial vascular graft applications. Biomacromol 14(4):1063–1071. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm3019467
Khalid MY, Al Rashid A, Arif ZU, Ahmed W, Arshad H (2021) Recent advances in nanocellulose–based different biomaterials: types, properties, and emerging applications. J Mater Res Technol 14:2601–2623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.07.128
Thakur V, Guleria A, Kumar S, Sharma S, Singh K (2021) Recent advances in nanocellulose processing, functionalization and applications: a review. Mater Adv 2(6):1872–1895. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MA00049G
Abou-Zeid RE, Hassan EA, Bettaieb F, Khiari R, Hassan ML (2015) Use of cellulose and oxidized cellulose nanocrystals from olive stones in chitosan bionanocomposites. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/687490
Al Hakkak J, Grigsby WJ, Kathirgamanathan K, Edmonds NR (2019) Generation of spherical cellulose nanoparticles from ionic liquid processing via novel nonsolvent addition and drying. Adv Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2081027
Hong F, Wei B, Chen L (2015) Preliminary study on biosynthesis of bacterial nanocellulose tubes in a novel double–silicone–tube bioreactor for potential vascular prosthesis. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/560365
Rigg-Aguilar P, Moya R, Oporto Velásquez GS, Vega Baudrit J, Starbird R, Puente Urbina A, Méndez D, Potosme LD, Esquivel M (2020) Micro–and nanofibrillated cellulose (MNFC) from pineapple (Ananas comosus) stems and their application on polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) and urea–formaldehyde (UF) wood adhesives. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1393160
Setyan A, Sauvain JJ, Riediker M, Guillemin M, Rossi MJ (2009) Characterization of surface functional groups present on laboratory–generated and ambient aerosol particles by means of heterogeneous titration reactions. J Aerosol Sci 40(6):534–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2009.01.008
Petrova OE, Sauer K (2017) High–performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)–based detection and quantitation of cellular c–di–GMP. Methods Mol Biol 1657:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7240-1_4
Ioelovich M (2017) Characterization of various kinds of nanocellulose. Handb Nanocellulose Cellul Nanocomposites 1:51–100. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527689972.ch2
Yingkamhaeng N, Intapan I, Sukyai P (2018) Fabrication and characterisation of functionalised superparamagnetic bacterial nanocellulose using ultrasonic–assisted in situ synthesis. Fiber Polym 19(3s):489–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-018-7738-6
Abba M, Nyakuma BB, Ibrahim Z, Ali JB, Razak SIA, Salihu R (2020) Physicochemical, morphological, and microstructural characterisation of bacterial nanocellulose from Gluconacetobacter xylinus BCZM. J Nat Fibers. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2020.1857896
Surma-Ślusarska B, Presler S, Danielewicz D (2008) Characteristics of bacterial cellulose obtained from Acetobacter xylinum culture for application in papermaking. Fibres Text East Eur 16(4):108–111
Bhattacharya A, Sadaf A, Dubey S, Singh RP, Khare SK (2021) Production and characterization of Komagataeibacter xylinus SGP8 nanocellulose and its calcite based composite for removal of Cd ions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(34):46423–46430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08845-7
Abol Fotouh D, Hassan MA, Shokry H, Roig A, Azab MS, Kashyout AEHB (2020) Bacterial nanocellulose from agro–industrial wastes: Low–cost and enhanced production by Komagataeibacter saccharivorans MD1. Sci Rep 10(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60315-9
Lee S, Abraham A, Lim ACS, Choi O, Seo JG, Sang BI (2021) Characterisation of bacterial nanocellulose and nanostructured carbon produced from crude glycerol by Komagataeibacter sucrofermentans. Bioresource Technol 342:125918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125918
Mohammadkazemi F, Azin M, Ashori A (2015) Production of bacterial cellulose using different carbon sources and culture media. Carbohyd Polym 117:518–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.10.008
Sijabat EK, Nuruddin A, Aditiawati P, Purwasasmita BS (2019) Synthesis and characterization of bacterial nanocellulose from banana peel for water filtration membrane application. J Phys Conf Ser 1230:012085. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1230/1/012085
Rosa MF, Medeiros ES, Malmonge JA, Gregorski KS, Wood DF, Mattoso LHC, Glenn G, Orts WJ, Imam SH (2010) Cellulose nanowhiskers from coconut husk fibers: Effect of preparation conditions on their thermal and morphological behavior. Carbohyd Polym 81(1):83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.01.059
Bolze J, Kogan V, Beckers D, Fransen M (2018) High–performance small–and wide–angle X–ray scattering (SAXS/WAXS) experiments on a multi–functional laboratory goniometer platform with easily exchangeable X–ray modules. Rev Sci Instrum 89(8):085115. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5041949
David K, Pu Y, Foston M, Muzzy J, Ragauskas A (2009) Cross–polarization/magic angle spinning (CP/MAS) 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis of chars from alkaline–treated pyrolyzed softwood. Energ Fuel 23(1):498–501. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef8004527
Cui Q, Zheng Y, Lin Q, Song W, Qiao K, Liu S (2014) Selective oxidation of bacterial cellulose by NO2–HNO3. RSC Adv 4(4):1630–1639
Coats AW, Redfern JP (1963) Thermogravimetric analysis. A review. Analyst 88(1053):906–924. https://doi.org/10.1039/AN9638800906
An SJ, Lee SH, Huh JB, Jeong SI, Park JS, Gwon HJ, Kang ES, Jeong CM, Lim YM (2017) Preparation and characterization of resorbable bacterial cellulose membranes treated by electron beam irradiation for guided bone regeneration. Int J Mol Sci 18(11):2236
Oliveira RL, Vieira JG, Barud HS, Assunção R, Filho G, Ribeiro SJ, Messadeqq Y (2015) Synthesis and characterization of methylcellulose produced from bacterial cellulose under heterogeneous condition. J Braz Chem Soc 26:1861–1870
George J, Ramana KV, Bawa AS (2011) Bacterial cellulose nanocrystals exhibiting high thermal stability and their polymer nanocomposites. Int J Biol MacroMol 48(1):50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.09.013
Reiniati I (2017) Bacterial cellulose nanocrystals: production and application. Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository. 4826. https://ir.lib.uwo.ca/etd/4826
Revin V, Liyaskina E, Nazarkina M, Bogatyreva A, Shchankin M (2018) Cost-effective production of bacterial cellulose using acidic food industry by-products. Braz J Microbiol 49:151–159
Jacquet N, Quievy N, Vanderghem C, Janas S, Blecker C, Wathelet B, Devaux J, Paquot M (2011) Influence of steam explosion on the thermal stability of cellulose fibres. Polym Degrad Stabil 96(9):1582–1588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.05.021
Mariano M, Cercená R, Soldi V (2016) Thermal characterization of cellulose nanocrystals isolated from sisal fibers using acid hydrolysis. Ind Crop Prod 94:454–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.09.011
Singhsa P, Narain R, Manuspiya H (2017) Bacterial cellulose nanocrystals (BCNC) preparation and characterization from three bacterial cellulose sources and development of functionalized BCNCs as nucleic acid delivery systems. ACS Appl Nano Mater 1(1):209–221. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.7b00105
Hanaor D, Michelazzi M, Leonelli C, Sorrell CC (2012) The effects of carboxylic acids on the aqueous dispersion and electrophoretic deposition of ZrO2. J Eur Ceram Soc 32(1):235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.08.015
Ioelovich M (2016) Comparative study of saccharification of biomass by various cellulolytic enzymes. ChemXpress 9(3):252–258
Evans R, Wallis AF (1989) Cellulose molecular weights determined by viscometry. J Appl Polym Sci 37(8):2331–2340. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1989.070370822
Li MC, Wu Q, Song K, Lee S, Qing Y, Wu Y (2015) Cellulose nanoparticles: structure–morphology–rheology relationships. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3(5):821–832. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00144
Dumanli AG (2017) Nanocellulose and its composites for biomedical applications. Curr Med Chem 24(5):512–528. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867323666161014124008
Li T, Chen C, Brozena AH, Zhu JY, Xu L, Driemeier C, Dai J, Rojas OJ, Isogai A, Wågberg L, Hu L (2021) Developing fibrillated cellulose as a sustainable technological material. Nature 590(7844):47–56. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-03167-7
Abbood IS, Aldeen Odaa S, Hasan KF, Jasim MA (2021) Properties evaluation of fiber reinforced polymers and their constituent materials used in structures–A review. Mater Today-Proc 43:1003–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.636
Thomas B, Raj MC, Joy J, Moores A, Drisko GL, Sanchez C (2018) Nanocellulose, a versatile green platform: from biosources to materials and their applications. Chem Rev 118(24):11575–11625
Nicu R, Ciolacu F, Ciolacu DE (2021) Advanced functional materials based on nanocellulose for pharmaceutical/medical applications. Pharmaceutics 13(8):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081125
Trache D, Tarchoun AF, Derradji M, Hamidon TS, Masruchin N, Brosse N, Hussin MH (2020) Nanocellulose: from fundamentals to advanced applications. Front Chem 8:392. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00392
Ghasemi S, Behrooz R, Ghasemi I, Yassar RS, Long F (2018) Development of nanocellulose–reinforced PLA nanocomposite by using maleated PLA (PLA–g–MA). Journal J Thermoplast Compos 31(8):1090–1101. https://doi.org/10.1177/0892705717734600
Bacakova L, Pajorova J, Bacakova M, Skogberg A, Kallio P, Kolarova K, Svorcik V (2019) Versatile application of nanocellulose: From industry to skin tissue engineering and wound healing. Nanomaterials 9(2):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020164
Österberg M, Cranston ED (2014) Special issue on nanocellulose. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 29(1):4–5. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2014-29-01-p004-005
Dugan JM, Gough JE, Eichhorn SJ (2013) Bacterial cellulose scaffolds and cellulose nanowhiskers for tissue engineering. Nanomedicine 8(2):287–298. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.12.211
He X, Xiao Q, Lu C, WangY ZX, Zhao J, Zhang W, Zhang X, Deng Y (2014) Uniaxially aligned electrospun all–cellulose nanocomposite nanofibers reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals: scaffold for tissue engineering. Biomacromol 15(2):618–627. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm401656a
Yan H, Huang D, Chen X, Liu H, Feng Y, Zhao Z, Dai Z, Zhang X, Lin Q (2018) A novel and homogeneous scaffold material: preparation and evaluation of alginate/bacterial cellulose nanocrystals/collagen composite hydrogel for tissue engineering. Polym Bull 75(3):985–1000
Piasecka-Zelga J, Zelga P, Gronkowska K, Madalski J, Szulc J, Wietecha J, Ciechańska D, Dziuba R (2021) Toxicological and sensitization studies of novel vascular prostheses made of bacterial nanocellulose modified with chitosan (MBC) for application as the tissue-engineered blood vessels. Regen Eng Transl Med 7(2):218–233
Ma N, Cheung DY, Butcher JT (2022) Incorporating nanocrystalline cellulose into a multifunctional hydrogel for heart valve tissue engineering applications. J Biomed Mater Res 110(1):76–91
Favi PM, Benson RS, Neilsen NR, Hammonds RL, Bates CC, Stephens CP, Dhar MS (2013) Cell proliferation, viability, and in vitro differentiation of equine mesenchymal stem cells seeded on bacterial cellulose hydrogel scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C 33(4):1935–1944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2012.12.100
Bhattacharya M, Malinen MM, Lauren P, Lou YR, Kuisma SW, Kanninen L, Lille M, Corlu A, GuGuen Guillouzo C, Ikkala O, Laukkanen A (2012) Nanofibrillar cellulose hydrogel promotes three–dimensional liver cell culture. J Control Release 164(3):291–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.06.039
Niculescu AG, Grumezescu AM (2022) An up–to–date review of biomaterials application in wound management. Polymers 14(3):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030421
Farahani M, Shafiee A (2021) Wound healing: from passive to smart dressings. Adv Healthc Mater 10(16):2100477. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202100477
Shah N, Ul Islam M, Khattak WA, Park JK (2013) Overview of bacterial cellulose composites: a multipurpose advanced material. Carbohyd Polym 98(2):1585–1598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.018
Kumar A, Han SS (2021) Efficacy of bacterial nanocellulose in hard tissue regeneration: a review. Materials 14(17):4777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14174777
Xi Loh EY, Fauzi MB, Ng MH, Ng PY, Ng SF, Ariffin H, Mohd Amin MCI (2018) Cellular and molecular interaction of human dermal fibroblasts with bacterial nanocellulose composite hydrogel for tissue regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10(46):39532–39543. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b16645
Silva NH, Garrido Pascual P, Moreirinha C, Almeida A, Palomares T, Alonso Varona A, Vilela C, Freire CS (2020) Multifunctional nanofibrous patches composed of nanocellulose and lysozyme nanofibers for cutaneous wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol 165:1198–1210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.249
Erdagi SI, Ngwabebhoh FA, Yildiz U (2020) Genipin crosslinked gelatin–diosgenin–nanocellulose hydrogels for potential wound dressing and healing applications. Int J Biol Macromol 149:651–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.279
Pajorova J, Skogberg A, Hadraba D, Broz A, Travnickova M, Zikmundova M, Honkanen M, Hannula M, Lahtinen P, Tomkova M, Bacakova L (2020) Cellulose mesh with charged nanocellulose coatings as a promising carrier of skin and stem cells for regenerative applications. Biomacromol 21(12):4857–4870. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.0c01097
Rees A, Powell LC, Chinga Carrasco G, Gethin DT, Syverud K, Hill KE, Thomas DW (2015) 3D bioprinting of carboxymethylated–periodate oxidized nanocellulose constructs for wound dressing applications. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/925757
Hakkarainen T, Koivuniemi R, Kosonen M, Escobedo Lucea C, Sanz Garcia A, Vuola J, Valtonen J, Tammela P, Mäkitie A, Luukko K, Yliperttula M (2016) Nanofibrillar cellulose wound dressing in skin graft donor site treatment. J Control Release 244:292–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.07.053
Koivuniemi R, Hakkarainen T, Kiiskinen J, Kosonen M, Vuola J, Valtonen J, Luukko K, Kavola H, Yliperttula M (2020) Clinical study of nanofibrillar cellulose hydrogel dressing for skin graft donor site treatment. Adv Wound Care 9(4):199–210
Ávila HM, Schwarz S, Feldmann EM, Mantas A, von Bomhard A, Gatenholm P, Rotter N (2014) Biocompatibility evaluation of densified bacterial nanocellulose hydrogel as an implant material for auricular cartilage regeneration. Appl Microbiol Biot 98(17):7423–7435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5819-z
Nimeskern L, Ávila HM, Sundberg J, Gatenholm P, Müller R, Stok KS (2013) Mechanical evaluation of bacterial nanocellulose as an implant material for ear cartilage replacement. J Mech Behav Biomed 22:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2013.03.005
Osorio M, Fernández Morales P, Gañán P, Zuluaga R, Kerguelen H, Ortiz I, Castro C (2019) Development of novel three-dimensional scaffolds based on bacterial nanocellulose for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: effect of processing methods, pore size, and surface area. J Biomed Mater Res A 107(2):348–359. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36532
Patil TV, Patel DK, Dutta SD, Ganguly K, Santra TS, Lim KT (2022) Nanocellulose, a versatile platform: from the delivery of active molecules to tissue engineering applications. Bioact Mater 9:566–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.07.006
Szustak M, Gendaszewska-Darmach E (2021) Nanocellulose-based scaffolds for chondrogenic differentiation and expansion. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.736213
Mc Givern S, Boutouil H, Al Kharusi G, Little S, Dunne NJ, Levingstone TJ (2021) Translational application of 3D bioprinting for cartilage tissue engineering. Bioeng 8(10):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8100144
Wang X, Wang Q, Xu C (2020) Nanocellulose–based inks for 3d bioprinting: Key aspects in research development and challenging perspectives in applications–A mini review. Bioeng 7(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7020040
Han C, Wang X, Ni Z, Ni Y, Huan W, Lv Y, Bai S (2020) Effects of nanocellulose on Alginate/Gelatin Bio–inks for extrusion–based 3D printing. BioResources 15(4):7357–7373. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.15.4.7357-7373
Nguyen D, Hägg DA, Forsman A, Ekholm J, Nimkingratana P, Brantsing C, Kalogeropoulos T, Zaunz S, Concaro S, Brittberg M, Lindahl A (2017) Cartilage tissue engineering by the 3D bioprinting of iPS cells in a nanocellulose/alginate bioink. Sci Rep–UK 7(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00690-y
Schwarz S, Kuth S, Distler T, Gögele C, Stölzel K, Detsch R, Boccaccini AR, Schulze Tanzil G (2020) 3D printing and characterization of human nasoseptal chondrocytes laden dual crosslinked oxidized alginate–gelatin hydrogels for cartilage repair approaches. Mater Sci Eng C 116:111189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.111189
Winkler T, Sass FA, Duda GN, Schmidt Bleek K (2018) A review of biomaterials in bone defect healing, remaining shortcomings and future opportunities for bone tissue engineering: The unsolved challenge. Bone Joint Res 7(3):232–243. https://doi.org/10.1302/2046-3758.73.BJR-2017-0270.R1
Mountziaris PM, Mikos AG (2008) Modulation of the inflammatory response for enhanced bone tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B-RE 14(2):179–186. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.teb.2008.0038
Torgbo S, Sukyai P (2020) Biodegradation and thermal stability of bacterial cellulose as biomaterial: The relevance in biomedical applications. Polym Degrad Stabil 179:109232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2020.109232
Sarkar C, Chowdhuri AR, Kumar A, Laha D, Garai S, Chakraborty J, Sahu SK (2018) One pot synthesis of carbon dots decorated carboxymethyl cellulose–hydroxyapatite nanocomposite for drug delivery, tissue engineering and Fe3+ ion sensing. Carbohyd Polym 181:710–718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.091
Ali A, Bano S, Poojary S, Chaudhary A, Kumar D, Negi YS (2022) Effect of cellulose nanocrystals on chitosan/PVA/nano β–TCP composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering application. J Biomat Sci-Polym E 33(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/09205063.2021.1973709
Sukul M, Nguyen TBL, Min YK, Lee SY, Lee BT (2015) Effect of local sustainable release of BMP2–VEGF from nano–cellulose loaded in sponge biphasic calcium phosphate on bone regeneration. Tissue Eng PT A 21(11–12):1822–1836. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tea.2014.0497
Carlström IE, Rashad A, Campodoni E, Sandri M, Syverud K, Bolstad AI, Mustafa K (2020) Cross–linked gelatin–nanocellulose scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater Lett 264:127326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.127326
Wei Z, Hong FF, Cao Z, Zhao SY, Chen L (2021) In situ fabrication of nerve growth factor encapsulated chitosan nanoparticles in oxidized bacterial nanocellulose for rat sciatic nerve regeneration. Biomacromol 22(12):4988–4999. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.1c00947
Thunberg J, Kalogeropoulos T, Kuzmenko V, Hägg D, Johannesson S, Westman G, Gatenholm P (2015) In situ synthesis of conductive polypyrrole on electrospun cellulose nanofibers: scaffold for neural tissue engineering. Cellulose 22(3):1459–1467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0591-5
Innala M, Riebe I, Kuzmenko V, Sundberg J, Gatenholm P, Hanse E, Johannesson S (2014) 3D Culturing and differentiation of SH–SY5Y neuroblastoma cells on bacterial nanocellulose scaffolds. Artif Cell Nanomed B 42(5):302–308. https://doi.org/10.3109/21691401.2013.821410
Du J, Tan E, Kim HJ, Zhang A, Bhattacharya R, Yarema KJ (2014) Comparative evaluation of chitosan, cellulose acetate, and polyethersulfone nanofiber scaffolds for neural differentiation. Carbohyd Polym 99:483–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.050
Min SK, Jung SM, Ju JH, Kwon YS, Yoon GH, Shin HS (2015) Regulation of astrocyte activity via control over stiffness of cellulose acetate electrospun nanofiber. In Vitro Cell Dev–AN 51(9):933–940. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9925-8
Naseri Nosar M, Salehi M, Hojjati Emami S (2017) Cellulose acetate/poly lactic acid coaxial wet–electrospun scaffold containing citalopram–loaded gelatin nanocarriers for neural tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol 103:701–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.054
Wu P, Zhao Y, Chen F, Xiao A, Du Q, Dong Q, Ke M, Liang X, Zhou Q, Chen Y (2020) Conductive hydroxyethyl cellulose/soy protein isolate/polyaniline conduits for enhancing peripheral nerve regeneration via electrical stimulation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:709. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00709
Cheng S, Zhang Y, Cha R, Yang J, Jiang X (2016) Water–soluble nanocrystalline cellulose films with highly transparent and oxygen barrier properties. Nanoscale 8(2):973–978. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR07647A
Muller D, Silva JP, Rambo CR, Barra GMO, Dourado F, Gama FM (2013) Neuronal cells’ behavior on polypyrrole coated bacterial nanocellulose three–dimensional (3D) scaffolds. J Biomat Sci-Polym E 24(11):1368–1377. https://doi.org/10.1080/09205063.2012.761058
Khalil HA, Jummaat F, Yahya EB, Olaiya NG, Adnan AS, Abdat M, Nasir NAM, Halim AS, Kumar U, Bairwan R, Suriani AB (2020) A review on micro-to nano-cellulose biopolymer scaffold forming for tissue engineering applications. Polymers Basel 12(9):2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092043
Ferreira FV, Otoni CG, Kevin J, Barud HS, Lona LM, Cranston ED, Rojas OJ (2020) Porous nanocellulose gels and foams: Breakthrough status in the development of scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater Today 37:126–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2020.03.003
Garai S, Sinha A (2014) Biomimetic nanocomposites of carboxymethyl cellulose–hydroxyapatite: Novel three dimensional load bearing bone grafts. Colloid Surface B 115:182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.11.042
Li K, Wang J, Liu X, Xiong X, Liu H (2012) Biomimetic growth of hydroxyapatite on phosphorylated electrospun cellulose nanofibers. Carbohyd Polym 90(4):1573–1581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.07.033
Park S, Park J, Jo I, Cho SP, Sung D, Ryu S, Park M, Min KA, Kim J, Hong S, Hong BH (2015) In situ hybridization of carbon nanotubes with bacterial cellulose for three–dimensional hybrid bioscaffolds. Biomaterials 58:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.04.027
Jonsson M, Brackmann C, Puchades M, Brattås K, Ewing A, Gatenholm P, Enejder A (2015) Neuronal networks on nanocellulose scaffolds. Tissue Eng PT C-Meth 21(11):1162–1170. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tec.2014.0602
de Oliveira Barud HG, da Silva RR, Borges MAC, Castro GR, Ribeiro SJL, da Silva BH (2021) Bacterial nanocellulose in dentistry: perspectives and challenges. Molecules 26(1):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010049
Voicu G, Jinga SI, Drosu BG, Busuioc C (2017) Improvement of silicate cement properties with bacterial cellulose powder addition for applications in dentistry. Carbohyd Polym 174:160–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.06.062
Anton-Sales I, Koivusalo L, Skottman H, Laromaine A, Roig A (2021) Limbal stem cells on bacterial nanocellulose carriers for ocular surface regeneration. Small 17(10):2003937. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202003937
Tummala GK, Rojas R, Mihranyan A (2016) Poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels reinforced with nanocellulose for ophthalmic applications: general characteristics and optical properties. J Phys Chem B 120(51):13094–13101. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b10650
Kupnik K, Primožič M, Kokol V, Leitgeb M (2020) Nanocellulose in drug delivery and antimicrobially active materials. Polymers-Basel 12(12):2825. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122825
Börjesson M, Westman G (2015) Crystalline nanocellulose—preparation, modification, and properties. In: Poletto M, Junior HLO (eds) Cellulose—fundamental aspects and current trends. IntechOpen, London. https://doi.org/10.5772/61899
Islam MT, Alam MM, Zoccola M (2013) Review on modification of nanocellulose for application in composites. Int J Innov Res Sci Eng Technol 2(10):5444–5451
Kolakovic R, Peltonen L, Laukkanen A, Hirvonen J, Laaksonen T (2012) Nanofibrillar cellulose films for controlled drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 82(2):308–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2012.06.011
Salimi S, Sotudeh Gharebagh R, Zarghami R, Chan SY, Yuen KH (2019) Production of nanocellulose and its applications in drug delivery: a critical review. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(19):15800–15827. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02744
Akhlaghi SP, Berry RC, Tam KC (2013) Surface modification of cellulose nanocrystal with chitosan oligosaccharide for drug delivery applications. Cellulose 20(4):1747–1764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9954-y
Müller A, Zink M, Hessler N, Wesarg F, Müller FA, Kralisch D, Fischer D (2014) Bacterial nanocellulose with a shape–memory effect as potential drug delivery system. Rsc Adv 4(100):57173–57184. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA09898F
Pandey M, Mohamad N, Amin MCIM (2014) Bacterial cellulose/acrylamide pH–sensitive smart hydrogel: development, characterization, and toxicity studies in ICR mice model. Mol Pharm 11(10):3596–3608. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp500337r
Lin N, Huang J, Chang PR, Feng L, Yu J (2011) Effect of polysaccharide nanocrystals on structure, properties, and drug release kinetics of alginate–based microspheres. Colloid Surface B 85(2):270–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.02.039
Zhang X, Huang J, Chang PR, Li J, Chen Y, Wang D, Yu J, Chen J (2010) Structure and properties of polysaccharide nanocrystal–doped supramolecular hydrogels based on cyclodextrin inclusion. Polymers-Basel 51(19):4398–4407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2010.07.025
Müller A, Ni Z, Hessler N, Wesarg F, Müller FA, Kralisch D, Fischer D (2013) The biopolymer bacterial nanocellulose as drug delivery system: Investigation of drug loading and release using the model protein albumin. J Pharm Sci 102(2):579–592. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.23385
Fey C, Betz J, Rosenbaum C, Kralisch D, Vielreicher M, Friedrich O, Metzger M, Zdzieblo D (2020) Bacterial nanocellulose as novel carrier for intestinal epithelial cells in drug delivery studies. Mater Sci Eng C 109:110613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110613
Silva NH, Mota JP, Santos de Almeida T, Carvalho JP, Silvestre AJ, Vilela C, Rosado C, Freire CS (2020) Topical drug delivery systems based on bacterial nanocellulose: Accelerated stability testing. Int J Mol Sci 21(4):1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041262
Moritz S, Wiegand C, Wesarg F, Hessler N, Müller FA, Kralisch D, Hipler UC, Fischer D (2014) Active wound dressings based on bacterial nanocellulose as drug delivery system for octenidine. Int J Pharm 471(1–2):45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.04.062
Alkhatib Y, Dewaldt M, Moritz S, Nitzsche R, Kralisch D, Fischer D (2017) Controlled extended octenidine release from a bacterial nanocellulose/Poloxamer hybrid system. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 112:164–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.11.025
Mensah A, Chen Y, Christopher N, Wei Q (2022) Membrane technological pathways and inherent structure of bacterial cellulose composites for drug delivery. Bioeng 9(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9010003
Abba M, Ibrahim Z, Chong CS, Zawawi NA, Kadir MRA, Yusof AHM, Razak SIA (2019) Transdermal delivery of crocin using bacterial nanocellulose membrane. Fiber Polym 20(10):2025–2031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-019-9076-8
Badshah M, Ullah H, Khan SA, Park JK, Khan T (2017) Preparation, characterization and in–vitro evaluation of bacterial cellulose matrices for oral drug delivery. Cellulose 24(11):5041–5052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1474-8
Yan H, Chen X, Feng M, Shi Z, Zhang W, Wang Y, Ke C, Lin Q (2019) Entrapment of bacterial cellulose nanocrystals stabilized Pickering emulsions droplets in alginate beads for hydrophobic drug delivery. Colloid Surface B 177:112–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.01.057
de Amorim JDP, de Souza KC, Duarte CR, da Silva DI, de Assis Sales Ribeiro F, Silva GS, de Farias PMA, Stingl A, Costa AFS, Vinhas GM, Sarubbo LA, (2020) Plant and bacterial nanocellulose: production, properties and applications in medicine, food, cosmetics, electronics and engineering. A rev Environ Chem Lett 18(3):851–869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-00989-9
Hasan N, Rahman L, Kim SH, Cao J, Arjuna A, Lallo S, Jhun BH, Yoo JW (2020) Recent advances of nanocellulose in drug delivery systems. J Pharm Investig 50(6):553–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-020-00499-4
Lee SH, Kim HJ, Kim JC (2019) Nanocellulose applications for drug delivery: a review. J For Environ Sci 35(3):141–149. https://doi.org/10.7747/JFES.2019.35.3.141
Jeevanandam J, Barhoum A, Chan YS, Dufresne A, Danquah MK (2018) Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: history, sources, toxicity and regulations. Beilstein J Nanotech 9(1):1050–1074. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.9.98
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other supports were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AC: Original draft, review and editing. SPM: Writing original draft, review and editing, supervision. PKD: Conceptualization, writing original draft, review and editing, revised manuscript preparation, supervision. BNS: Review and editing. AKS: Original draft and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non–financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandana, A., Mallick, S.P., Dikshit, P.K. et al. Recent Developments in Bacterial Nanocellulose Production and its Biomedical Applications. J Polym Environ 30, 4040–4067 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02507-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02507-0