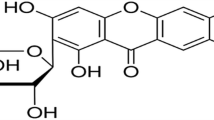
Abstract
Natural colors particularly animal-based colorants are employed in the field of cosmetics, food, and flavors and also gaining popularity in textiles, due to their soothing nature. In this study, the microwave-assisted extraction of colorant from cochineal insects for dyeing of bio-mordanted silk has been carried out. Acidic, methanolic, and acidified methanol solubilized media were used to extract the natural colorant from cochineal under microwave irradiation for 1–6 min. Bio-mordants have been employed at optimized conditions to make the process greener and sustainable. It is found that acid solubilized extract of pH 4, employed at 55 °C for 55 min containing 5 g/100 mL of Glauber’s salt as exhausting agent has given high color strength onto microwave-treated silk fabric. Suggested ISO standards for colorfastness have revealed that bio-mordants have given excellent color depth and excellent rating of fastness properties, compared with chemical mordants used. It is found that microwave treatment has not only improved the dyeing behavior of colorant extracted from cochineal in acid solubilized medium but also enhanced the color characteristics onto bio-mordanted silk fabric.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeel S, Zuber M, Rehman FU, Zia KM (2018a) Microwave-assisted extraction and dyeing of chemical and bio-mordanted cotton fabric using harmal seeds as a source of natural dye. Environ Sci Pollu Res 25(11):11100–11110
Adeel S, Naseer K, Javed S, Mahmmod S, Tang RC, Amin N, Naz S (2018b) Microwave-assisted improvement in dyeing behavior of chemical and bio-mordanted silk fabric using safflower (Carthamustinctorius L) extract. J Nat Fibers 17(1):55–65
Adeel S, Zia KM, Abdullah M, Rehman FU, Salman M, Zuber M (2019a) Ultrasonic assisted improved extraction and dyeing of mordanted silk fabric using neem bark as source of natural colourant. Nat Prod Res 33(14):2060–2072
Adeel S, Rehman FU, Iqbal MU, Habib N, Kiran S, Zuber M, Zia KM, Hameed A (2019b) Ultrasonic assisted sustainable dyeing of mordanted silk fabric using arjun (Terminalia arjuna) bark extracts. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 38(s1):S331–S339
Ammayappan L, Shakyawar DBB (2016) Dyeing of carpet woolen yarn using natural dye from cochineal. J Nat Fiber 13(1):42–53
Ariede MB, Candido TM, Jacome ALM, Velasco MVR, de Carvalho JCM, Baby AR (2017) Cosmetic attributes of algae-a review. Algal Res 25:483–487
Azeem M, Iqbal N, Mir RA, Adeel S, Batool F, Khan AA, Gul S (2019a) Harnessing natural colorants from algal species for fabric dyeing: a sustainable eco-friendly approach for textile processing. J App Phycol 31:3941–3948
Azeem M, Adeel S, Habib N, Rehman FU, Zahoor AF, Saeed M, Amin N, Liaqat S, Hussaan M (2019b) Sustainable utilization of ultrasonic radiation in extraction and dyeing of wool fabric using logwood (Haematoxylumcampechianum) extracts. TekstilKonfeksiyon 29(2):181–185
Baaka N, Haddar W, Ticha MB, Amorim MTP, M’Henni MF (2017) Sustainability issues of ultrasonic wool dyeing with grape pomace colourant. Nat Prod Res 31(14):1655–1662
Bouatay F, Baaka N, Shahid A, Mhenni MF (2019) A novel natural source ViciafabaL. membranes as colourant: development and optimization of the extraction process using response surface methodology (RSM). Nat Prod Res 33(1):59–65
Campana MG, Robles García NM, Tuross N (2015) America’s red gold: multiple lineages of cultivated cochineal in Mexico. Ecol Evol 5(3):607–617
Chen C, Zhang B, Huang Q, Fu X, Liu RH (2017) Microwave-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Moringa oleifera Lam leaves: characterization and hypoglycemic activity. Ind Crop Prod 100:1–11
Cooksey CJ (2018) The red insect dyes: carminic, kermesic and laccaic acids and their derivatives. Biotech Histochem:1–8
Ebrahimi I, Gashti MP (2016) Extraction of polyphenolic dyes from henna, pomegranate rind, and Pterocarya fraxinifolia for nylon 6 dyeing. Color Technol 132:162–176
Giacomini F, Menegazzo MAB, dos Santos JCO, Arroyo PA, de Barros MASD (2017) Ecofriendly dyeing of silk with extract of yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis). Text Res J 87:829–837
Grande GA, Giansetti M, Pezzin A, Rovero G, Sicardi S (2017) Use of the ultrasonic cavitation in wool dyeing process: effect of the dye-bath temperature. Ultrason Sonochem 35:276–284
Haddar W, Ticha BM, Meksi N, Guesmi A (2018) Application of anthocyanins as natural dye extracted from Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata f. rubra: dyeing studies of wool and silk fibres. Nat Prod Res 32:141–148
Haggag K, El-Molla MM, Mahmoued ZM (2014) Dyeing of cotton fabrics using reactive dyes by microwave irradiation technique. Ind J Fibre Text Res 39:406–410
Haji A, Mehrizi MK, Sharifzadeh J (2016a) Dyeing of wool with aqueous extract of cotton pods improved by plasma treatment and chitosan: optimization using response surface methodology. Fiber Polym 17(9):1480–1488
Haji A, Qavamnia SS, Bizhaem FK (2016b) Salt free neutral dyeing of cotton with anionic dyes using plasma and chitosan treatments. Ind Text 67(2):109–113
Irimia-Vladu M, Głowacki ED, Troshin PA, Schwabegger G, Leonat L, Susarova DK, Razumov VF (2012) Indigo-a natural pigment for high performance ambipolar organic field effect transistors and circuits. Adv Mater 24(3):375–380
İşmal ÖE, Yıldırım L (2019) Metal mordants and biomordants. Impact Pros Green Chem Text Technol Woodhead Publishing, p 57–82
Khan MA, Islam SU, Mohammad F (2017) Investigating the combined effect of natural and metal salt mordants on coloring potential of indian rhubarb (Rheum emodi) natural dye. J Nat Fibers 14(2):196–204
Kiumarsi A, Gashti MP, Salehi P, Dayeni M (2017) Extraction of dyes from Delphinium zalil flowers and dyeing silk yarns. J Text I108:66–70
Li Q, Wu S, Wang C, Yi Y, Zhou W, Wang H, Tan Z (2017) Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of sinomenine from Sinomenium acutum using magnetic ionic liquids coupled with further purification by reversed micellar extraction. Process Biochem 58:282–288
Nakpathom M, Somboon B, Narumol N, Mongkholrattanasit R (2017) Fruit shells of Camellia oleifera Abel as natural colourants for pigment printing of cotton fabric. Pigm Resin Technol 46(1):56–63
Pandey AK, Ahmad MS, Rahim NA, Tyagi VV, Saidur R (2019) Natural sensitizers and their applications in dye-sensitized solar cell. Environ Biotech Sustain Future. Springer, Singapore, pp 375–401
Patil DM, Akamanchi KG (2017) Microwave assisted process intensification and kinetic modelling: extraction of camptothecin from Nothapodytes nimmoniana plant. Ind Crop Prod 98:60–67
Rather L, Akhter S, Padder RA, Hassan QP, Hussain M, Khan MA, Mohammad F (2017) Colorful and semi durable antioxidant finish of woolen yarn with tannin rich extract of Acacia nilotica natural dye. Dyes Pigments 139:812–819
Rather LJ, Khan MA, Mohammad F (2019) Bio-mordanting potential of Acacia nilotica (Babul) in conjunction with Kerria lacca and Rheum emodi natural dyes. J Nat Fiber 16(2):275–286
Ren Y, Gong J, Wang F, Li Z, Zhang J, Fu R, Lou J (2016) Effect of dye bath pH on dyeing and functional properties of wool fabric dyed with tea extract. Dyes Pigments 134:334–341
Salimian S, Moghaddam MK, Safi S, Mortazavi SM (2016) Properties of wool dyed with pinecone powder as a by-product colorant. Ind J Fibre Text Res 41:173–179
Shabbir M, Islam SU, Bukhari MN, Rather LJ, Khan MA, Mohammad F (2017) Application of Terminalia chebula natural dye on wool fiber-evaluation of color and fastness properties. Text Cloth Sustain 2(1):1
Shahid I, Rather LJ, Shabbir M, Bukhari MN, Shahid M, Khan MA, Mohammad F (2016) Bi and tri metal salt combinations plus colorants extracted from timber industry waste as effective dyeing materials to produce novel shades on wool. J Nat Fiber 14(4):586–596
Shams Nateri A, Dehnavi E, Hajipour A, Ekrami E (2016) Dyeing of polyamide fibre with cochineal natural dye. Pigm Resin Technol 45(4):252–258
Singh P, Borthakur A, Singh R, Awasthi S, Pal DB, Srivastava P, Mishra PK (2017) Utilization of temple floral waste for extraction of valuable products: a close loop approach towards environmental sustainability and waste management. Pollution 3(1):39–45
Wang F, Gong J, Zhang X, Ren Y, Zhang J (2018) Preparation of bio-colorant and eco-dyeing derived from polyphenols based on laccase-catalyzed oxidative polymerization. Polymers 10(2):196
Wathon MH, Beaumont N, Benohoud M, Blackburn RS, Rayner CM (2019) Extraction of anthocyanins from Aronia melanocarpa skin waste as a sustainable source of natural colorants. Color Technol 135(1):5
Yılmaz Şahinbaşkan B, Karadag R, Torgan E (2018) Dyeing of silk fabric with natural dyes extracted from cochineal (Dactylopius coccus Costa) and gall oak (Quercusinfectoria Olivier). J Nat Fibers 15(4):559–574
Yin Y, Jia J, Wang T, Wang C (2017) Optimization of natural anthocyanin efficient extracting from purple sweet potato for silk fabric dyeing. J Clean Prod 149:673–679
Yusuf M, Shahid M, Khan MI, Khan SA, Khan MA, Mohammad F (2015) Dyeing studies with henna and madder: a research on effect of tin (II) chloride mordant. J Saudi Chem Soc 19(1):64–72
Yusuf M, Mohammad F, Shabbir M, Khan MA (2017a) Eco-dyeing of wool with Rubiacordifolia root extract: assessment of the effect of Acacia catechu as bio-mordant on color and fastness properties. Text Cloth Sust 2(1):10
Yusuf M, Khan SA, Shabbir M, Mohammad F (2017b) Developing a shade range on wool by madder (Rubiacordifolia) root extract with gallnut (Quercus infectoria) as biomordant. J Nat Fibers 14(4):597–607
Yusuf M, Shabbir M, Mohammad F (2017c) Natural colorants: historical, processing and sustainable prospects. Nat Prod Bioprospect 7(1):123–145
Zia KM, Adeel S, Khosa MK, Aslam H, Zuber M (2019) Influence of ultrasonic radiation on extraction and green dyeing of mordanted cotton using neem bark extract. J Ind Eng Chem 77:317–322
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amin, N., Rehman, Fu., Adeel, S. et al. Sustainable application of cochineal-based anthraquinone dye for the coloration of bio-mordanted silk fabric. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 6851–6860 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06868-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06868-3